PEDRO MORAIS
Scientific Researcher
(2017~2023)
① Effect of Mindfulness Meditation on Brain Electrical Activity (Concentration, Motor Response and Emotional Reaction);
② Electrophysiological Signal Processing (EDA, ECG and EEG);
③ Research of Anxiety, Depression and Stress States with Statistical & Time-Series Analysis;
④ Machine Learning & Python Programming;
⑤ Brain-Machine/Computer Interfaces (BMI/BCI).
The Effect of Mindfulness Meditation on Electrophysiological Activity: Assessment of Concentration State, Emotional Control, and Quality of Life
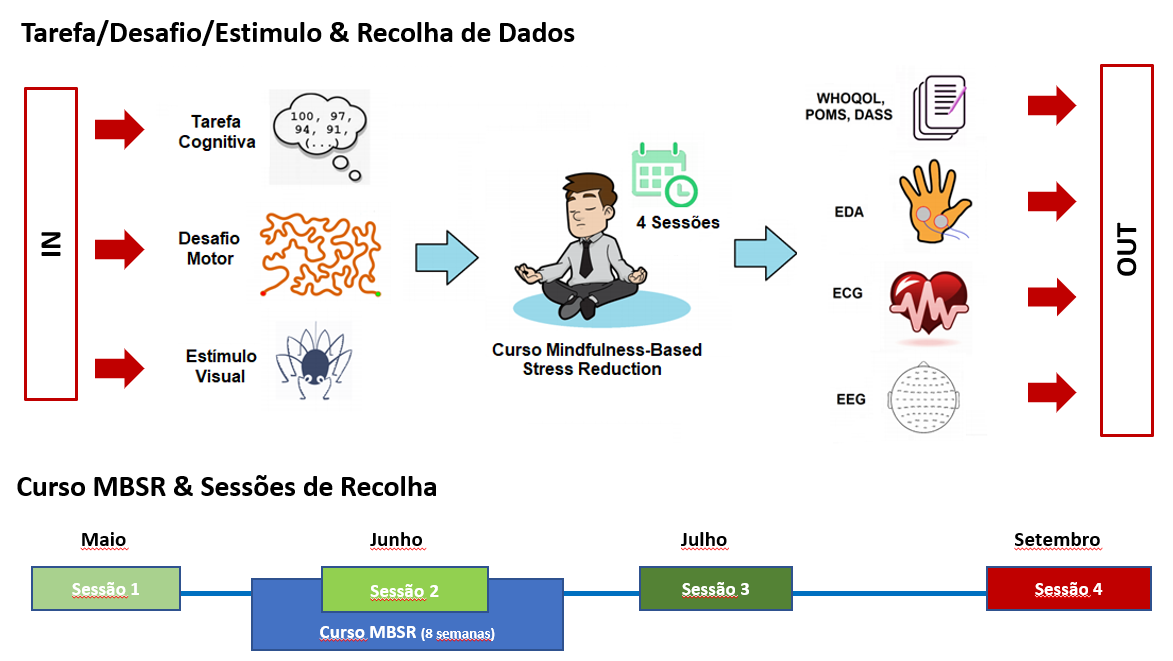
Being healthy is much more than not being ill. It is essentially living day-to-day life in physical and mental well-being. A modern, increasingly hectic and demanding society makes this goal more difficult. Today, a large part of the population suffers from depression, anxiety and/or stress. This public health problem, recently intensified by COVID-19, urgently needs a solution. The beneficial effect of the continued practice of Mindfulness meditation can contribute to a better quality of life for the individual, living the present with full attention. Using a cognitive task, a motor challenge and a visual stimulus, 25 volunteers (mean age = 26, SD = 7, 9 male) were evaluated in a period of 4 months, in which, during 8 weeks, they attended the Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) course. In the 4 scheduled sessions (Pre, Peri, Post- MBSR and follow-up 2 months later) three electrophysiological signals are simultaneously collected: electroencephalogram (EEG), electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrodermal activity (EDA). In parallel, three questionnaires are completed: quality of life (WHOQOL), mood state profile (POMS) and anxiety, depression and stress scale (DASS). In the DASS analysis to the total participants, the anxiety state decreases -66.0% (p<0.001), depression -51% (p<0.001) and stress -52.0% (p<0.001). In the POMS survey, the global index of Total Mood Disturbance (TMD) registers a reduction of -19.0% (p<0.001). As regards the WHOQOL-100 questionnaire, there is an average increase of 11.2% (p<0.001) in quality of life. In the cognitive task there is, between the beginning and the end of the MBSR course, an expressive decrease in the mean amplitude of EDA in the order of -64.5% (p<0.001), a decrease of - 5.8% (p<0.05) in the mean heart rate (HR) and, in the EEG data, a very relevant increase of 148.1% (p<0.001) in the mean power of the α rhythm. In the motor challenge, the changes in the biosignals do not show statistical significance, however, a decrease in the mean errors occurred from 4.52 to 2.88 during the course is recorded. Finally, the visual stimulus reports a decrease of -43.9% (p=0.06) in EDA amplitude and -2.0% (p=0.57) in HR. The study of emotional reactions through EEG, combining valence levels with arousal, indicates an increase from -0.47 to 0.10 in positive feeling and from -0.17 to 0.02 in the degree of intensity of emotion. The analysis of these data suggests that the continued practice of Mindfulness meditation tends to increase the individual's state of concentration, motor skills, emotional control and quality of life. It promotes a healthy mind, characterised by self-regulation of attention and a reduction in states of anxiety, depression and/or stress, which is accompanied by significant electrophysiological changes. It can thus be used as a means of prevention or help in situations of psychological disorders that affect a large part of the population.
O Efeito da Meditação Mindfulness na Actividade Electrofisiológica: Avaliação do Estado de Concentração, Controlo Emocional e Qualidade de Vida
Ser saudável é muito mais do que não estar doente. É essencialmente viver o dia-a-dia sob um bem-estar físico e mental. Uma sociedade moderna, cada vez mais agitada e exigente, dificulta esse objectivo. Presentemente, grande parte da população sofre de depressão, ansiedade e/ou stress. Este problema de saúde pública, agravado recentemente pelo COVID-19, carece de uma solução urgente. O efeito benéfico da prática continuada de meditação Mindfulness poderá contribuir para uma melhor qualidade de vida do indivíduo, vivendo o presente em atenção plena. Recorrendo a uma tarefa cognitiva, a um desafio motor e a um estímulo visual, são avaliados 25 voluntários (média idades = 26 anos, DP = 7, 9 masculinos), num período de 4 meses, no qual, durante 8 semanas, frequentaram o curso Mindfulnes-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR). Nas 4 sessões programadas (Pré, Peri, Pós-MBSR e follow-up 2 meses depois) são recolhidos, simultaneamente, três sinais electrofisiológicos: electroencefalograma (EEG), electrocardiograma (ECG) e actividade electrodérmica (EDA). Paralelamente, são preenchidos três questionários: qualidade de vida (WHOQOL), perfil de estado de humor (POMS) e escala de ansiedade, depressão e stress (DASS). Na análise DASS ao total de participantes, o estado de ansiedade diminui -66.0% (p<0.001), depressão -51% (p<0.001) e stress -52.0% (p<0.001). No inquérito POMS, o índice global de Perturbação Total de Humor (PTH) regista uma redução de -19.0% (p<0.001). Relativamente ao questionário WHOQOL-100, apresenta um aumento médio de 11.2% (p<0.001) na qualidade de vida. Na tarefa cognitiva verifica-se, entre o início e o final do curso MBSR, uma diminuição expressiva da média da amplitude de EDA na ordem dos -64.5% (p<0.001), um decréscimo de -5.8% (p<0.05) na média da frequência cardíaca (HR) e, nos dados de EEG, um aumento muito relevante de 148.1% (p<0.001) na potência média do ritmo α. No desafio motor, as alterações nos biosinais não apresentam significado estatístico, no entanto, regista-se um decréscimo na média dos erros ocorridos de 4.52 para 2.88 durante o percurso. Por último, o estímulo visual reporta um decréscimo de -43.9% (p=0.06) na amplitude de EDA e de -2.0% (p=0.57) em HR. O estudo de reacções emocionais através de EEG, combinando níveis de valência com excitação, indica o aumento de -0.47 para 0.10 do sentimento positivo e de -0.17 para 0.02 do grau de intensidade da emoção. A análise destes dados sugere que a prática continuada da meditação Mindfulness tende a aumentar o estado de concentração, destreza motora, controlo emocional e qualidade de vida do indivíduo. Promove uma mente saudável, caracterizada pela autorregulação da atenção e pela diminuição de estados de ansiedade, depressão e/ou stress, a qual é acompanhada por alterações electrofisiológicas significativas. Poderá, assim, ser utilizada como um meio de prevenção ou auxílio em situações de distúrbios psicológicos que afectam grande parte da população. A agregação de métodos e o estudo efectuado de forma longitudinal, correlacionando a análise dos registos eletrofisiológicos com os inquéritos realizados, permite consolidar as conclusões obtidas representando uma abordagem original neste domínio científico.